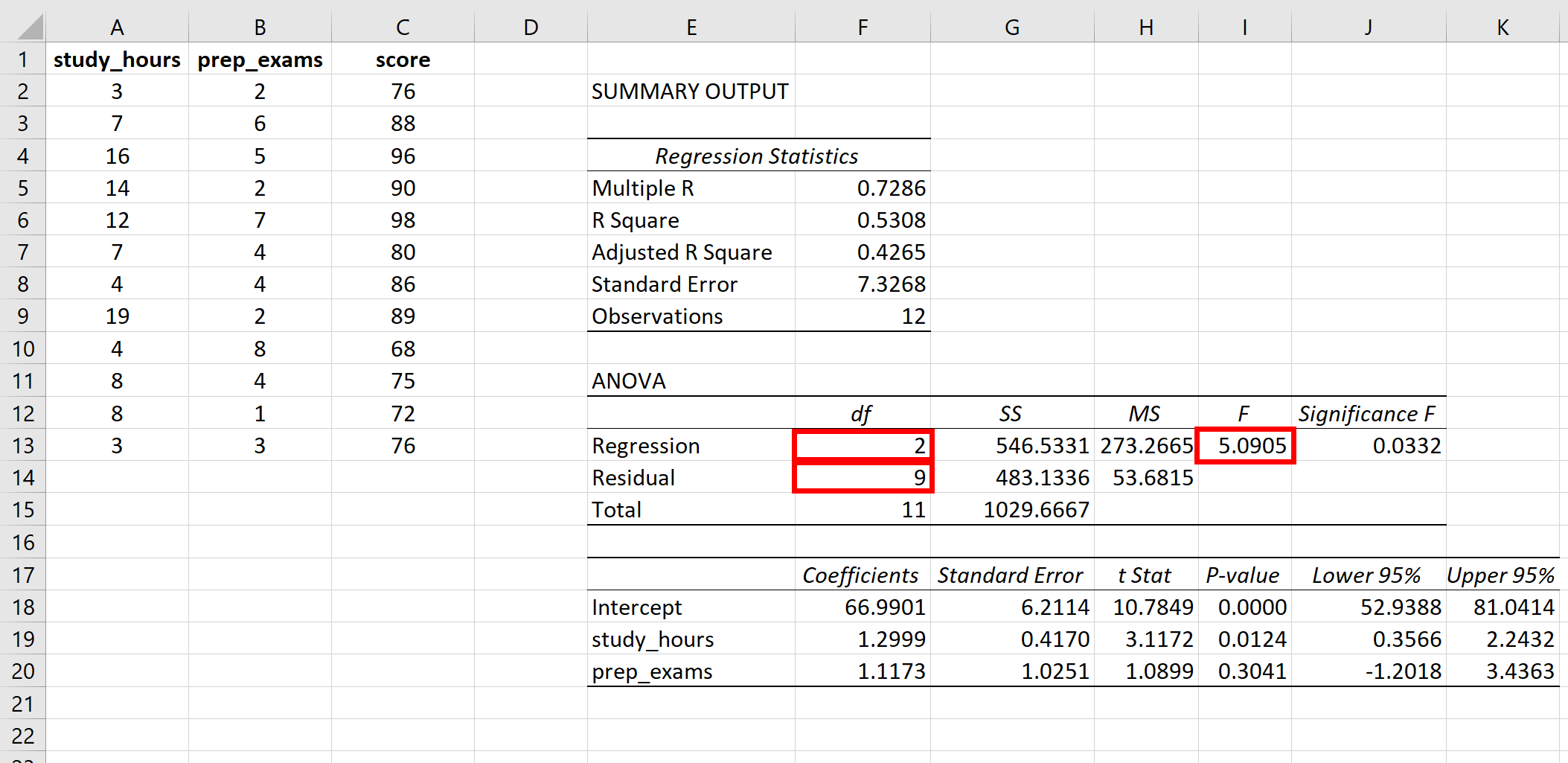
5 Easy Steps to Create a Standard Curve in Excel
Creating a standard curve in Excel is essential for various scientific and analytical applications where you need to establish a relationship between concentration and measurement signal. Whether you're working in biochemistry, environmental science, or any field requiring quantitative analysis, this guide will provide you with a clear, step-by-step approach to setting up your standard curve effectively. Here's how you can do it in five easy steps:
Step 1: Prepare Your Data
The first step is gathering and organizing your data. A standard curve requires:
- Known concentrations of your standard
- Measurements or signals corresponding to these concentrations
For example, if you’re measuring enzyme activity, your data might look like this:
| Concentration | Absorbance |
|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.1 |
| 1.0 | 0.15 |
| 2.0 | 0.2 |
| 3.0 | 0.25 |
📝 Note: Ensure your measurements are precise and taken under consistent conditions for accuracy.
Step 2: Enter Data into Excel
Now, input your data into an Excel sheet:
- Label Column A as “Concentration” and Column B as “Signal” or your measurement unit.
- Enter your known concentrations in column A and corresponding signals in column B.
Step 3: Plot Your Data
After inputting your data:
- Select both columns (A and B).
- Go to the “Insert” tab.
- Choose “Scatter” chart from the “Charts” group.
- Select the scatter plot with smooth lines.
This plot visually represents the relationship between concentration and signal.
Step 4: Add a Trendline and Get the Equation
With your scatter plot created:
- Right-click on any data point.
- Select “Add Trendline.”
- Choose “Linear” for most standard curves, but this might vary based on your data.
- Check the box for “Display Equation on chart” to get your standard curve equation.
Step 5: Use Your Standard Curve
Your equation can now be used to calculate unknown concentrations:
- Input the signal of your unknown sample into the equation.
- Solve for concentration. For example, if your equation is y = 0.05x + 0.1 and your signal is 0.4, you can solve for x to find the concentration.
🔹 Note: Ensure your equation’s R² value (shown in the trendline options) is close to 1 to ensure a good fit.
By following these steps, you've successfully created a standard curve in Excel, enabling you to quantify unknown samples with high accuracy. This approach not only streamlines your analytical process but also provides a reliable framework for future experiments or analyses. Whether you're quantifying enzymes, pollutants, or any measurable parameter, Excel's straightforward tools make creating standard curves a breeze.
What is the purpose of a standard curve?
+A standard curve is used to establish a relationship between the concentration of a substance and a measurable response, such as absorbance or fluorescence. It allows you to quantify unknown samples by comparing their response to known standards.
How can I ensure the accuracy of my standard curve?
+Ensure accuracy by using precise measurements, selecting standards within a relevant range, keeping conditions consistent, and checking the R² value to confirm the goodness of fit.
What should I do if my standard curve doesn’t fit well?
+Recheck your data for errors or try different curve fitting options in Excel, like polynomial or logarithmic, to see if they better match your data’s behavior.
Related Terms:
- Standard curve graph generator
- Standard curve calculator
- Standard curve excel template
- standard curve graph maker
- standard curve in excel tutorial
- qpcr standard curve excel